3D Graphics Programming with QuickDraw 3D 1.5.4
Previous | QD3D Book | Overview | Chapter Contents | Next |
Trigrids
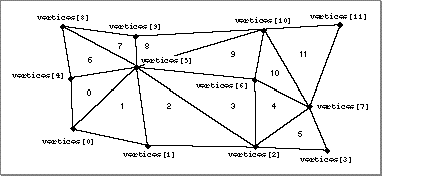
Figure 11 shows a trigrid.
Data Format
Uns32 numUVertices
Uns32 numVVertices
Point3D vertices[numUVertices * numVVertices]
- numUVertices
- The number of vertices in the u parametric direction.
- numVVertices
- The number of vertices in the v parametric direction.
- vertices[]
- An array of vertices. The size of this array must equal the number of vertices of the trigrid. Vertices are to be listed in a rectangular order, first in the direction of increasing v , then in the direction of increasing u . That is, the vertex having parametric coordinates ( u , v ) precedes the vertex having parametric coordinates ( u ', v ') if and only if either u < u ', or u = u ' and v < v '.
Description
A trigrid is a grid composed of triangular facets. The triangulation should be serpentine (that is, quadrilaterals are divided into triangles in an alternating fashion) to reduce shading artifacts when using Gouraud or Phong shading. Attributes may be assigned to each vertex and to each facet of a trigrid, and also to the entire trigrid.
Child Objects
Vertex attribute set list (optional), face attribute set list (optional), attribute set (optional). A face attribute set list may be used to assign attributes to the facets of a trigrid. The number of facets of a trigrid is the same as the number of its vertices. The vertices and facets of a trigrid are indexed in the manner shown by Figure 11 . The vertex index prefers u to v and prefers 0 to 1; thus, it follows the canonical lexicographical ordering of the points in uv parametric space. The facet index is less easily defined but is readily apprehended. Consider first the serpentine path through the trigrid along the diagonals belonging to facets of the trigid. Now consider the alternative serpentine path composed of segments connecting all and only those vertices not on the first path. The second path passes through each facet and intersects all of the diagonals on the first path. The facets of the trigrid are numbered in the order that they would be encountered by a traveler along the second serpentine path.
Example
Container (
TriGrid (
3 #numUVertices
4 #numVVertices
2 0 0 2 1 0 2 2 0 2 3 0
1 0 0 1 1 0 1 2 0 1 3 0
0 0 0 0 1 0 0 2 0 0 3 0
)
Container (
FaceAttributeSetList (12 include 61 3 5 7 9 11)
Container (
AttributeSet( )
DiffuseColor (1 1 1)
)
.
.
.
Container (
AttributeSet( )
DiffuseColor (1 1 1)
)
)
Container (
AttributeSet ( )
DiffuseColor ( 0 0 0 )
)
)
© 1997 Apple Computer, Inc.
Previous | QD3D Book | Overview | Chapter Contents | Next |